Population, Sample & Variable
Population, Sample and Variable are three key terms that are inevitable in any Statistical Analysis. To find the difference between these terms let’s take the example of a sales analysis in a mobile shop
In this case the customers of the mobile shop constitute the study group, which we call the Population. So, the size of the population can be in tens, hundreds or thousands. Higher the population size, more reliable is the result.
So, when we have a bigger population, it is always difficult and time consuming to collect data from each individual in the population. So, in such cases, we use various sampling techniques in order to create a Sample that represent the characteristics and features of the real population. Sample is a subset of population. It can be defined as a set of individuals that can resemble the properties or characteristics of the population from which it was selected.
Sometimes the sample selected can be misleading if it does not reflect the characteristics and features of a population. This is called ‘Paradox of Sampling’. For example, if we include only those individuals who are willing to respond and leave those who are in hurry or are not willing to respond then the information that we collect may have a negative impact on our analysis. In short, the representativeness of the sample is an inevitable factor for a proper statistical analysis.
A Variable can be defined as any features or characteristics that helps us to distinguish between two individuals in a sample. For instance, let’s take the example of a mobile shop. Different customers have different preference like some may need better camera, some may need better battery backup and soon. Variables can be classified as followed:
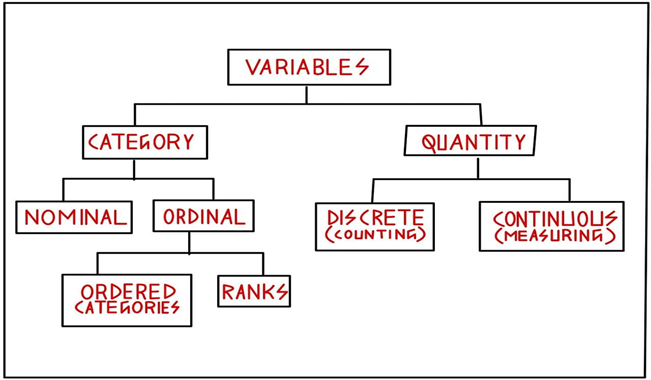
Categorical Variables
Any variable that divides a sample into categories can be termed as Categorical variables. There are two types of categorical variables, namely, nominal or ordinal.
Nominal Variable: In Latin, ‘nominalis’ means ‘of a name’. So as the name suggests it gives name to different variables. For example, brand of mobile phones.
Ordinal Variable: Ordinal variable refers to variable used to rank or order a sample. Its is again divided into two – Ordered categories (e.g.: Poor, Good, very good and excellent) and Ranked category (e.g.: First, second, third)
Quantity Variable
Any variable attributes that are quantifiable or that can be measured can be defined as Quantity variable. It is mainly of two categories:
Discrete Variables: These variables are countable. For example, number of mobile phones, a person own can be 1,2,3 and so on. It can never be 2.05 or 9.54
Continuous Variable: These variables are measurable. For example, dimension of a cell phone, speed of a vehicle , etc.